Case Study
Hash functions are highly related with computer security (e.g., cryptography). For example, when you want to download some file from the Internet, you will probably notice a magic string (e.g., sha512) which can be used to verify the integrity of the file.
In fact, such string is computed by a hash function based on the bits of a file. If the results are matched, we can say the file is not changed by anyone due to the consistency of a hash function.
- Java's MessageDigest provides many cryptographic hash functions to find hash value of a text.
- Python's hashlib implements a common interface to many different secure hash and message digest algorithms.
But detailed discussion on cryptography is out of the scope of this book.
Hash vs. RBT
Is hashing faster than searching in red-black BSTs?
It depends on the type of the key, which determines the cost of computing hash code versus the cost of comparison. For typical key types, these costs are similar, so hashing will be significantly faster, since it uses only a constant number of operations.
But it is important to remember that this question is moot if you need ordered operations, which are not efficiently supported in hash tables.
Cockoo Hashing
Cuckoo hashing is a form of open addressing with worst-case constant lookup time. The basic idea of cuckoo hashing is to resolve collisions by using two hash functions instead of only one. This provides two possible locations in the hash table for each key. For simplicity, here we only consider keys.
lookup()
Cuckoo hashing uses two hash tables \(T_1\) and \(T_2\), and assuming \(m\) be the length of each table. The lookup operation is as follows:
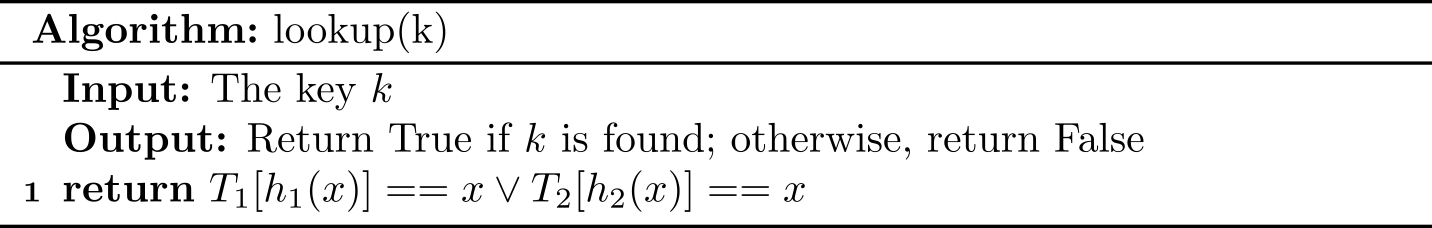
insert()
The most interesting part of Cuckoo hashing is its insertion.
- If the slot \(h_1(k)\) of table \(T_1\) is not occupied, the new key \(k\) is inserted at that cell.
- Otherwise, the preoccupied key \(k'\) gets removed, and \(k\) is inserted at \(T_1[h_1(x)]\). The removed key \(k'\) is inserted into \(T_2\) by following the same procedure.
To avoid the possible infinite iteration, a Max-Loop is specified. If the loop exceeds the fixed threshold, then we conduct a rehash() operation by newer hash functions.